The digital age is ushering in revolutionary changes in the financial sector globally, with digital currencies at the forefront of this transformation.
Introduction
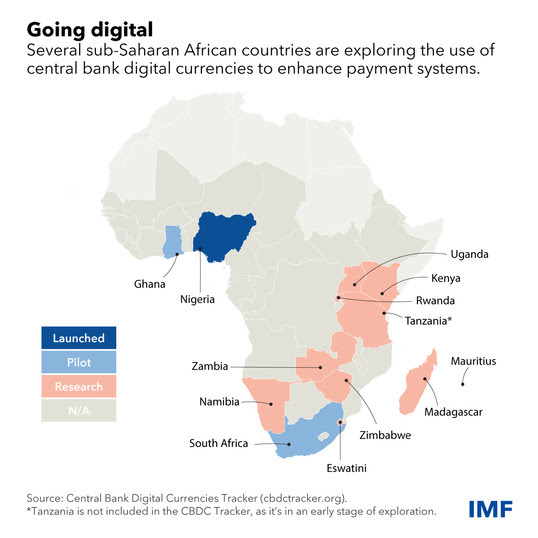
In Ghana, a nation where economic vibrancy is matched by its potential for digital innovation, the adoption of digital currencies represents a significant leap towards financial inclusivity.
This paper delves into how digital currencies could reshape the financial landscape in Ghana, making economic participation more accessible to all layers of society.
The Current State of Financial Inclusion in Ghana
Despite Ghana’s economic advancements, a considerable portion of its population remains on the periphery of the formal financial system.
Challenges such as limited access to banking facilities, prohibitive transaction fees, and a pervasive mistrust in traditional financial institutions have stifled the country’s financial inclusion efforts.
As a result, a significant number of Ghanaians are either unbanked or underbanked, especially in rural areas.
Digital Currency: A Pathway to Inclusion
Digital currencies, encompassing both cryptocurrencies and Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs), offer a promising solution to these challenges.
They stand out for their ability to ensure financial services are accessible, affordable, efficient, and secure:
- Accessibility: Through mobile technology, digital currencies can reach the remotest parts of Ghana, bringing financial services to those previously unreachable.
- Lower Costs: By bypassing traditional banking infrastructures, digital currencies can significantly reduce transaction costs.
- Increased Efficiency: Transactions executed with digital currencies are completed swiftly, enhancing the overall user experience.
- Security and Trust: Leveraging blockchain technology, digital currencies provide a secure transaction environment, potentially increasing their adoption.
Ghana’s Move Towards a Digital Currency
The Bank of Ghana is at the forefront of this digital revolution, exploring the e-cedi, a CBDC aimed at complementing the physical cedi.
This initiative is not merely a testament to Ghana’s commitment to embracing digital innovation but also a strategic move to democratise financial access across the nation.
The e-cedi is designed to be user-friendly, even for those with basic feature phones, ensuring that the benefits of digital currencies extend to the entire population.
Opportunities Presented by Digital Currency in Ghana
The introduction of digital currency in Ghana opens a plethora of opportunities:
- Enhanced Financial Services: It paves the way for innovative financial products that cater to the unbanked and underbanked.
- Economic Empowerment: Easy access to digital currencies can empower SMEs and individuals, spurring economic growth.
- Improved Remittances: Digital currencies promise to streamline remittance processes, making them quicker and cheaper.
Challenges and Considerations
However, the path to a fully inclusive digital currency system in Ghana is fraught with challenges:
- Digital Literacy and Infrastructure: Ensuring widespread digital literacy and robust internet infrastructure is crucial for the success of digital currencies.
- Regulatory Framework: A sound regulatory environment is essential to mitigate risks related to money laundering, financial stability, and consumer protection.
- Market Adoption: Encouraging widespread acceptance of digital currency among the public and businesses remains a critical hurdle.
Conclusion
The advent of digital currency in Ghana heralds a new era of financial inclusion, promising to integrate the unbanked and underbanked into the formal economy. While challenges lie ahead, the potential benefits of digital currencies — in terms of accessibility, cost, and economic empowerment — are too significant to ignore.
As Ghana continues its path towards digital currency adoption, it sets an example of how technology can be harnessed to build a more inclusive financial system.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What is digital currency?
Digital currency is electronic money that exists in a digital form. Unlike traditional currencies, digital currencies can be transferred between entities or users with the help of technology like the Internet or mobile networks.
There are two main types: cryptocurrencies, like Bitcoin, and Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs), which are issued and regulated by a country’s central bank.
How does digital currency promote financial inclusion?
Digital currency promotes financial inclusion by making financial services accessible to people who are unbanked or underbanked, especially in remote areas. It reduces transaction costs, improves the efficiency of payments, and provides secure transaction mechanisms, encouraging more people to participate in the formal financial system.
What is the e-cedi?
The e-cedi is a digital currency initiative by the Bank of Ghana aimed at complementing the existing physical Ghanaian cedi. It is a form of Central Bank Digital Currency (CBDC) designed to be accessible and usable by the general public, including those without access to traditional banking services.
How can digital currency benefit SMEs in Ghana?
Digital currency can significantly benefit SMEs by providing them with more accessible and cheaper financing options, enabling easier transactions with customers and suppliers, and offering secure mechanisms for handling payments. These advantages can help SMEs grow and expand their operations more efficiently.
What are the challenges of adopting digital currency in Ghana?
The main challenges include ensuring sufficient digital literacy among the population, developing the necessary infrastructure to support digital currency transactions, creating a robust regulatory framework to address potential risks, and encouraging widespread acceptance and use of digital currencies among individuals and businesses.
How is the Ghanaian government ensuring the security of digital transactions?
The Ghanaian government, through the Bank of Ghana, is developing regulations and frameworks to ensure the security of digital transactions. This includes leveraging blockchain technology for its security benefits, implementing strict KYC (Know Your Customer) and anti-money laundering measures, and continuously monitoring and updating security protocols to guard against fraud and cyber threats.
Can digital currency replace traditional money in Ghana?
While digital currency offers numerous benefits and has the potential to become widely used, it is unlikely to completely replace traditional money shortly. Both forms of currency are expected to coexist, with digital currency serving as a complement to traditional forms of money, enhancing the overall efficiency and inclusivity of the financial system in Ghana.

This paper is authored by Dr. Shirley Ayangbah, an accomplished scholar with expertise spanning international law (International Economic Law), economics, and sustainable development. With a Ph.D. in International Law focused on integrating sustainable development into investment treaties, and advanced degrees in economics and international relations.